New Technologies to Improve the Civil Protection in Sardinia Region (Italy)

28 August 2023
Salvatore Cinus, Head of Risk Forecasting Sector at Regione Autonoma Della Sardegna
Fabrizia Soi, Head of the Forest Fire Forecasting Sector at Regione Autonoma Della Sardegna
As we know, civil protection systems operates to prepare and coordinate interventions aimed to protect the population and the heritage in a risk area. These tasks are carried out both in “peace time”, for example by means of risk forecast activities and during calamity events.

In Italy the most important national law reference is the Legislative Decree n. 1/2018 “Civil Protection Code” (D. Lgs. n. 1/2018 “Codice della protezione civile”), which article 2 defines the Civil Protection targets:
- Forecasting
- Prevention
- Emergency management
- Emergency overcoming phase
In Sardinia the direction and coordination of the Civil Protection are entrusted to the President of the Region, who exercises these functions through the Directorate General for Civil Protection (DGPC).
The Directorate General for Civil Protection of Sardinia Region (DGPC-RAS) implements and coordinates all the activities that are aimed, at regional level at protecting lives, properties, settlements, animals and the environment from damage - or the danger of damage - resulting from natural or man-made disasters.
The following picture shows how DGPC is organised in the territory:
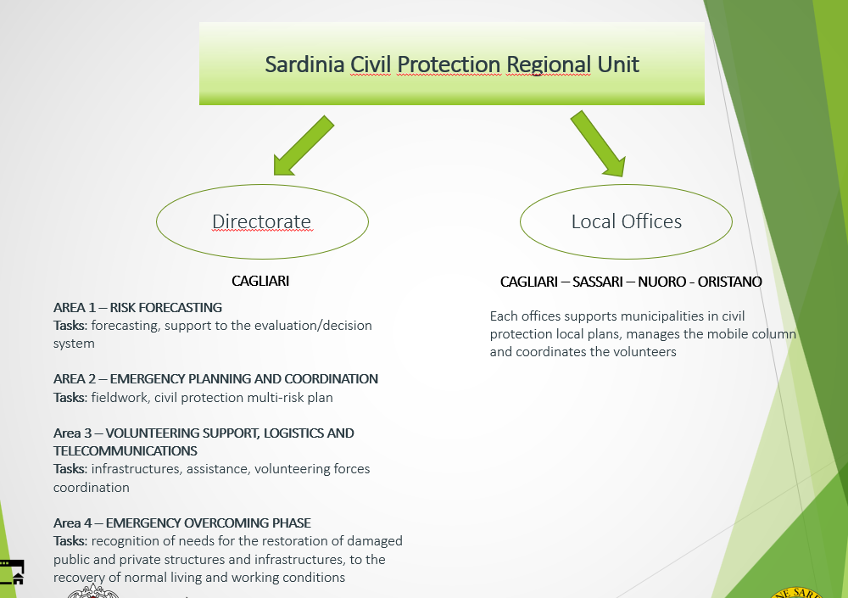
The DGPC RAS has an in-depth experience in forest fires, prevention and planning of hydrological and hydraulic risks: regarding these natural hazards, the DGPC RAS can provide sound knowledge, based on territorial and risk characteristics pertaining to Sardinia's specificity.
To pursue its goals, DGPC-RAS is supported by two main operational rooms.
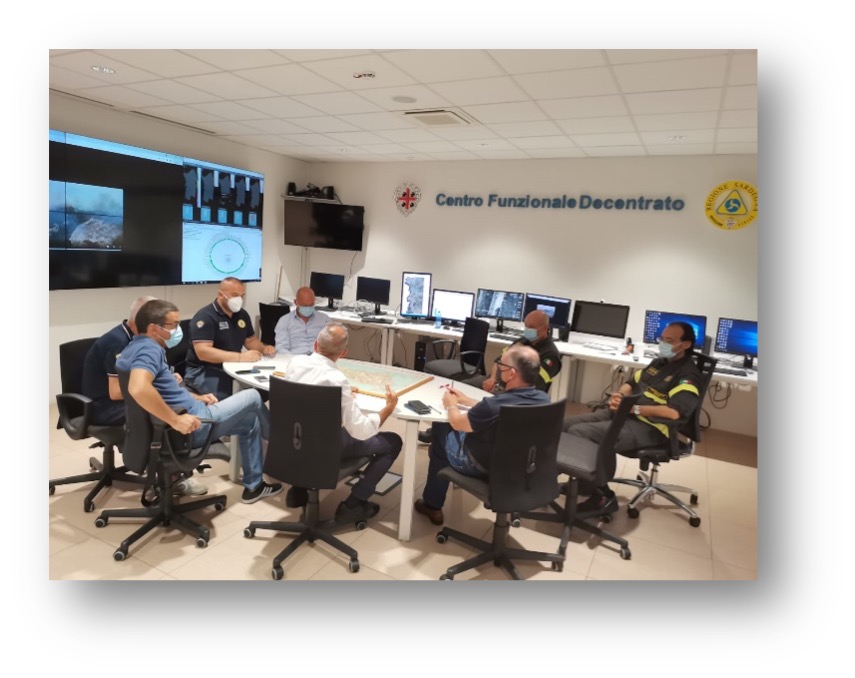
The firs one is called the decentralised operational Centre (CFD) and it is part of the national early warning system. The CFD is organised by risk areas in order to support the response of the civil protection system to all foreseeable risks. Currently, there are two operating areas, one on the field of geological and hydraulic risk and the other on forest fires, with the goal to provide a continuous service, every day of the year and, when necessary, 24 hours a day, in order to support the decisions of the competent authorities regarding alert and emergency management and to assist the operational needs of civil protection systems.
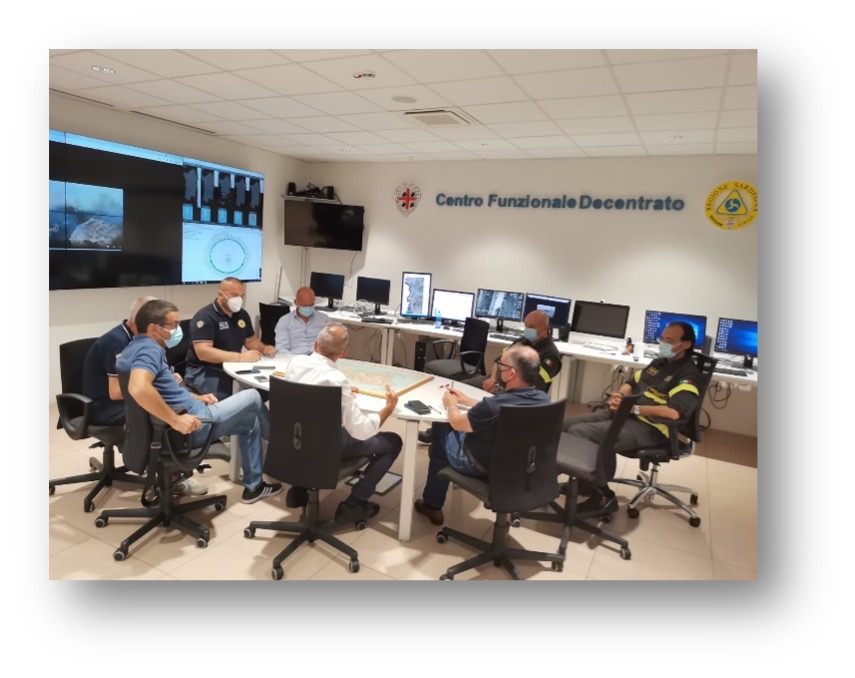

The second room is called Integrated Regional Operations Room (SORI) and constantly monitors and supports the territory (It works 24h/day every day of the year. When necessary, the operations Room follows the emergencies, alerts and activates the various Civil Protection actors that can contribute to overcome them.
In relations to the wildfire risk, the operations rooms is called Unified and permanent Operations Room (SOUP). . Its tasks are related to ensure:
- the activity of regional forces against wildfires, in coordination with the national forces.
- the support of helicopters and Canadairs when necessary.

New technologies, as Artificial Intelligence, support civil protection activities and permit to be smarter in forecasting risk and more generally in peace time, quicker and effective during interventions.
It is undeniable that DGPC-RAS is constantly in search of technical solutions to improve Natural Disaster Management, as the ones enabled by cutting-edge technologies and AI.
In order to be more effective some critical aspects are listed below, aspects that if satisfied can improve significantly civil protection service.
- CFD needs to predict scenarios adequately, and for this reason forecasting models should be very accurate and during the monitoring phase magnitude of the events should be precisely measured, even using radar and remote sensing.
- Decision takers needs to know accurately the field scenario as soon as it happens if possible.
- Decision command flow and support to local population, by means of SORI/SOUP, should be tempestive during a calamity.
- it would be useful to have footage in the SOUP room that could be acquired by the teams on the ground to understand the extent of the event and how it is developing.
- needs of Drone flights for reconnaissance (even at night) and assistance to operations night and day
- Create real-time maps for data sharing for public authorities. For example, it was found in some emergencies that the same reconnaissance activity had been done by different authorities (PC/Fire Department).
- Effective information to the population on risks before and during expected heavy rain events
- Continuity of communication channels – and sharing of the same between different relief forces operating in the field
- Effectively and continuously exchange information and data between coordination rooms and field teams
- Possibility of carrying out reconnaissance activities in difficult weather conditions
The previous described gaps and desiderata are goals for DGPC.
The participation in the Horizon European TEMA project as an end-user is an opportunity for DGPC to reach a better level service.
Improvements should be reached even by a massive use of drones both in peace time for reconnaissance that during calamities.
Very recently the General Directorate for Civil Protection of Sardinia Region organised drone pilot course aimed to obtain Unmanned Aerial Systems license A1/A2/A3 license.
After a theoretical part, the training had implied a focus on photogrammetric survey. Divided into teams, pilots carried out operational missions by simulating emergency conditions and the typical scenarios of complex situations, such as the survey of buildings, bridges, roads and dams, as well as detailed analyses of wooded areas or riverbeds, during day and night.
Soon courses for “specific” drone licenses will be arranged.
These new professionals will be a fundamental tool both in prevention and emergency management activities.
In Tema project consortium are involved 20 partners, divided in two types tightly linked: technology partners and end-users. For DGPC will be a good opportunity to support the developing of new technologies aimed to support how its institutional tasks are satisfied.
The platform that will be developed during the project could be tested by DGPC, Forestry Corp of Sardinia region, Forestas Agency and Sardinian fire brigades in order to create a common repository and facilitate exchange of information between field teams and operations rooms.
Some technologies could be effectively tested during the following 4 years in Sardinia, among them:
- Gathering of data to reconstruct field scenario - Use of geo-social media data. This technology is offered by “Plus” and permits to georeferenced textual data and imagery from social networks. Singular posts with high relevance content would be shown. Information (footage, image, maps) highly updated from the site of disaster could be monitored and shown to the operation rooms.
- XR based visualization system (Northdocks partner) could be used for breaking down and rearrange technical data into clear and easy to understand visualizable parts for operation rooms and first responders devices.
- Smartdesk (Kamk partner) could support the exchange of information between operations rooms and teams in the field. It is an interactive large scale touchscreen table equipped with an user-friendly application for overall situation management in control room to get big picture of current situation, make annotations and send them (control rooms-on site units), visualize processed data of floods and fires.
- Satellite based flood and forest fire detection and assessment (DLR-DFD partner) could help in reconstruct scenario.
- Various technologies to facilitate communication and exchange data among teams in the field operations rooms, etc. as semantic segmentation, federated learning, etc.
The tema Project will allow to DGPC to confront with the other partners for 4 years, to know how new tools could be used for its institutional tasks and to adopt new technologies in the operational rooms.

