Artificial Intelligence for Sustainability: What is the Role of AI in Advancing Targets for Sustainability

8 November 2023
Felipe Taylor Murta, Project Manager and Research Associate at the Lisbon Council
Climate change is impacting economic, social, and environmental systems across the globe and its consequences are expected to continue in the foreseeable future. As European cities face warmer, drier, and wetter climates that result in natural hazards, extreme weather events such as floods, storms, and heatwaves account for 85,000 to 145,000 human fatalities across Europe.
Against this backdrop, adaptation policies have been launched to help Europe mitigate the impacts and prepare for them [1], while Artificial Intelligence (AI) and other technologies will play an important role in climate adaptation.
This article briefly discusses the roles that AI can play in climate change mitigation, adaptation, and resilience. Departing from a presentation on how AI can be used to tackle climate change, it presents how AI use has been embedded in sustainable agendas and how TEMA is part of the effort to explore the full potential of this technology.
AI as a tool to tackle climate change
AI has a great potential to assess, predict, and mitigate the effects of climate change as it gathers, interprets, and completes large and complex datasets on emissions and climate impact, which provides better solutions for informed decision-making. It can be useful for:
- Transforming raw data into actionable information;
- Optimising complex systems;
- Improving prediction;
- Accelerating scientific modelling and discovery[2].
Figure 1 presents a more specific application for AI to combat climate change[3]:
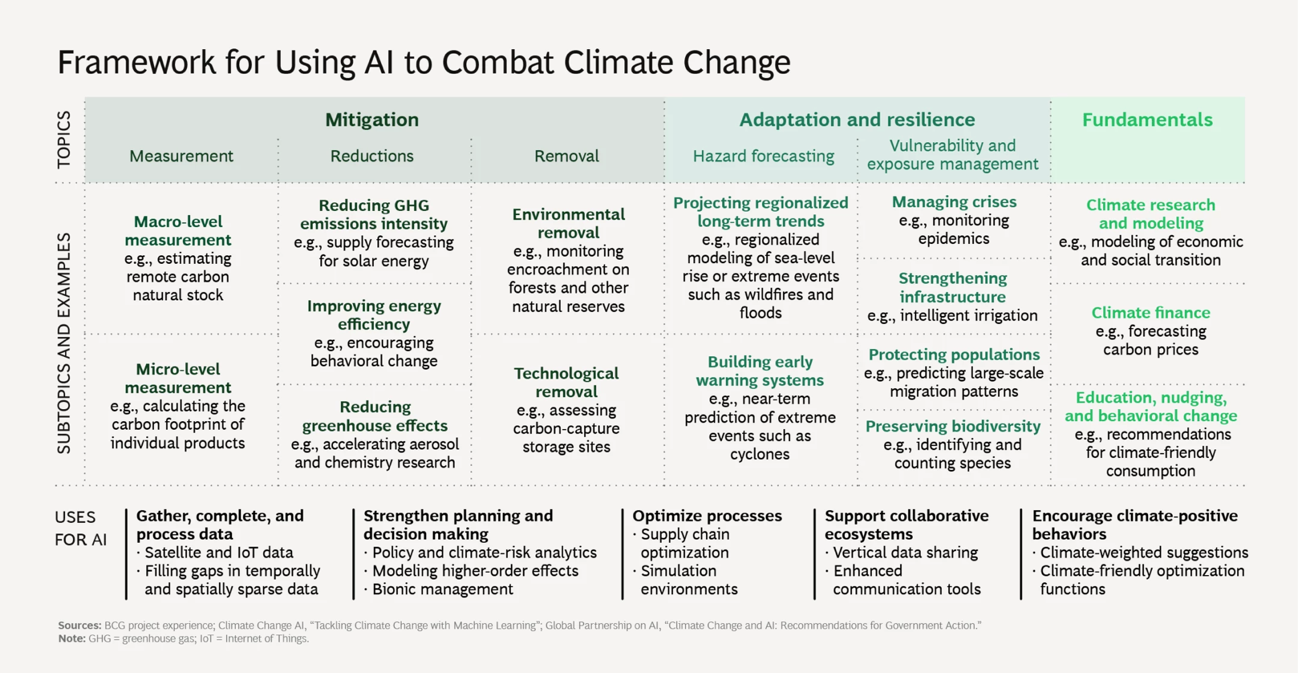
AI in the green agenda
Considering the importance of AI for sustainability, this section seeks to describe how AI is advancing sustainable development.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
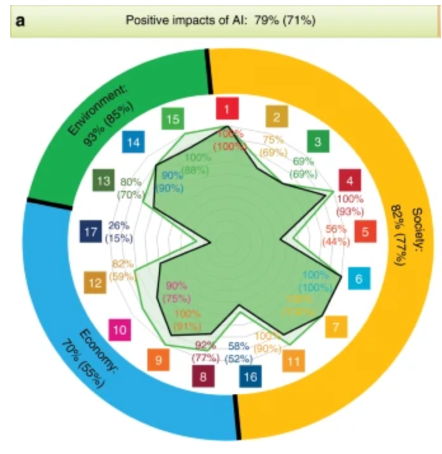
The SDGs were defined under the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in 2015, encompassing 17 goals and 169 targets. AI can act as an enabler for 134 targets across all SDGs, spanning across social, economic and environmental issues. Although the paper reports positive and negative impacts of AI-based technology use, this article focuses on the positive aspects.
Societal outcomes
A total of 67 targets could benefit from the use of AI-based technologies, covering SDG1 on no poverty, SDG4 on quality education, SDG6 on clean water and sanitation, SDG7 on affordable and clean energy, SDG11 on sustainable cities, and SDG16 on peace, justice, and strong institutions. In this sense, AI can, for instance, work in favour for the supply of food, water, health, and energy services for the population, and support the transition for smarter cities and circular economy adoption, which is tightly linked to the efficient use of resources.
Economic outcomes
The technological advances provided using AI can generate positive impacts on 42 targets, including SDG8 on decent work and economic growth, SDG9 on industry, innovation, and infrastructure, SDG10 on inequalities reduction, SDG12 on responsible consumption and production, and SDG17 on partnerships for the goals. AI can help increase productivity, identify sources of inequalities, and predict human behaviours.
Environmental outcomes
AI-based technologies can work as an enabler for 25 targets under the environmental group. Namely, it refers to SDG13 on climate action, SGD14 on life below water, and SDG15 on life on land. AI enables the analysis of large-scale interconnected databases, which benefits the development of joint actions for preserving the environment. For instance, it can process large amounts of satellite images to support decision-making and environmental planning to avoid desertification and reverse negative trends, as well as support low-carbon energy systems by integrating renewable energy and energy efficiency.
Figure 2 provides an overview on how AI can generate positive impacts for societal, economic, and environmental outcomes for the SDGs[4]:
AI in the European Green Deal and its potential for the Twin Green and Digital Transition
The European Green Deal seeks to promote fairness and prosperity and an efficient, competitive, and more sustainable economy for Europe. AI has the potential to contribute to the European strategies through many axes that tackle environmental challenges.
- Scientific knowledge on the environment is essential for tackling environmental challenges, and AI can contribute to better information for relevant decision-making. The Earth Observation programmes, such as Copernicus and New Space, produce large amounts of environmental data, and ai systems can provide a more effective, efficient, and timely monitoring of the environmental systems, the impacts they have been facing, and their trends.
- AI can inform and encourage responsible business behaviour by aligning financing decisions with sustainable development. AI can improve resource, energy, and material efficiency, and produce impacts on supply and value-chains through Industry 4.0 solutions, such as automation of processes and integration of data along the value-chain.
- AI can inform and encourage responsible consumer behaviour by providing information to consumers and raising awareness about the manufacturing process and nudging consumers towards a more sustainable consumption.
- AI can strengthen environmental administration and participatory governance through regulatory technology, which can support the implementation and enforcement of EU environmental law[5].
Understanding the potential of AI, the European Commission has built a EU approach to help building a resilient Europe for the Digital Decade based on AI solutions in a human-centric and trustworthy way. Investments in AI have been implemented through the Horizon Europe and Digital Europe programmes, to which the Commission plans to invest €1 billion per year[6].
TEMA and AI for Sustainability
“Trusted Extremely Precise Mapping and Prediction for Emergency Management” (TEMA) project, is one of the many European-funded projects in Horizon Europe that use AI for mitigating and tackling the effects of climate change. AI technologies can be harnessed for better natural disaster management (NDM) to support disaster prevention and preparedness, and TEMA is exploring the automation of precise semantic 3D mapping and disaster evolution prediction to achieve NDM goals in near-real-time for floods and forest-fires.
In the scope of its activities, the project is preparing a webinar that will contribute to stakeholder engagement and community building for the creation of synergies that will support the use of AI as a response to climate change effects European citizens are facing.
The high-level Webinar “AI 4 Sustainability” will count with the participation of other European-funded projects to discuss the subject and join forces into one main goal. It will be convened on November 15th, from 10:00-11:00am (CET).
If you are interested in joining our efforts, you can register for the webinar here.
Bibliography:
[1] https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/topics/in-depth/climate-change-impacts-risks-and-adaptation#:~:text=Climate%20change%20is%20impacting%20Europe%27s,impacts%2C%20particularly%20on%20vulnerable%20groups.
[2] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eKm1BUeDolg
[3] https://www.bcg.com/publications/2022/how-ai-can-help-climate-change
[4] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-14108-y
[5] https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/STUD/2021/662906/IPOL_STU(2021)662906_EN.pdf
[6] https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/european-approach-artificial-intelligence

